
Electric Vehicle Charging Cables Market Analysis By Power Supply (Alternate Charging (AC), Direct Charging (DC)), By Cable Length (Below 5 meters, 6 meters to 10 meters, Above 10 meters), By Shape Outlook (Straight Cable, Coiled Cable), By Application (Private Charging, Public Charging), By Charging Level (Level 1, Level 2, Level 3) & Forecast By 2031
- PUBLISHED ON
- 2024-06-06
- NO OF PAGES
- 263
- CATEGORY
- Automotive & Transportation
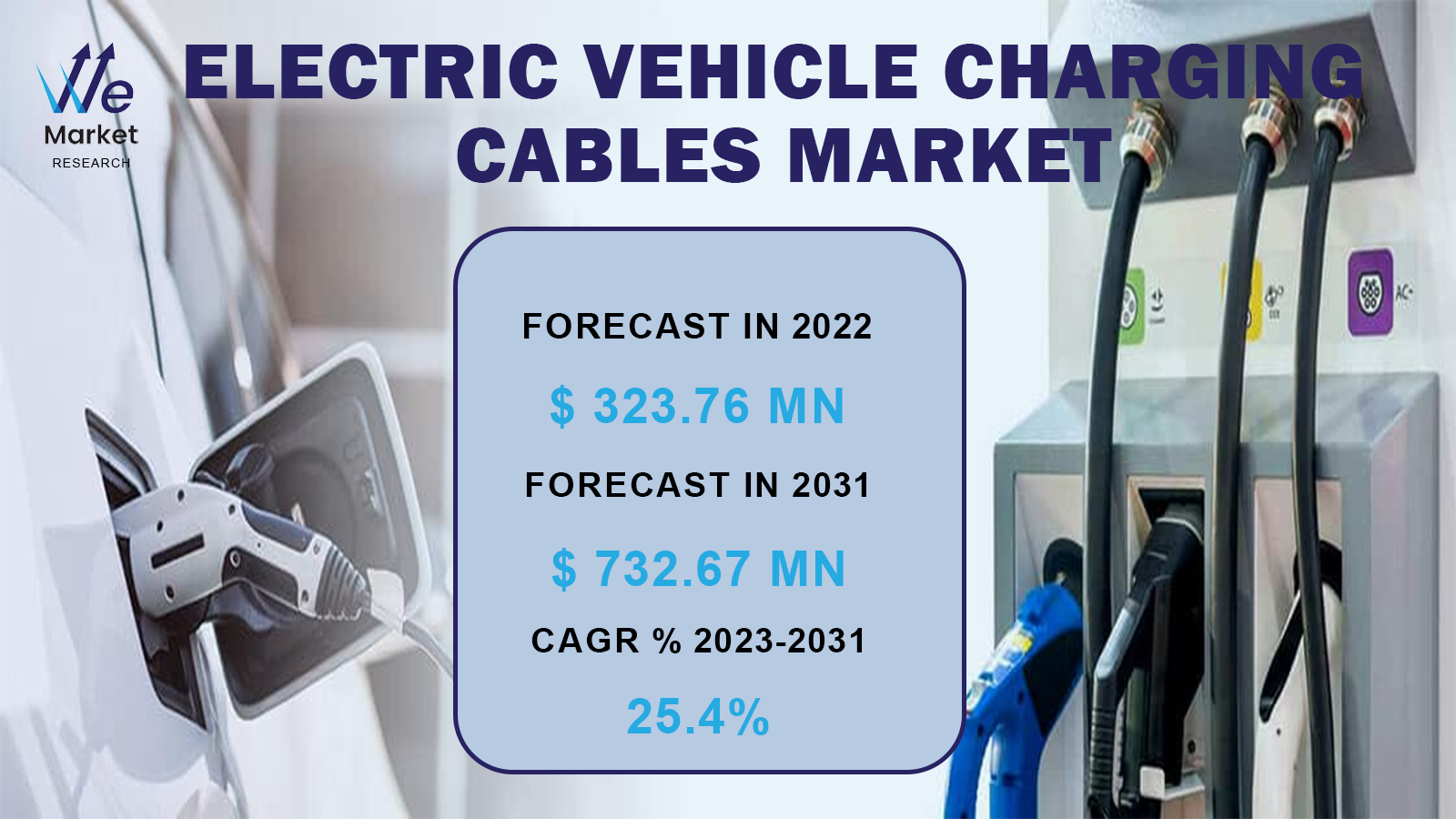
Electric Vehicle Charging Cables Market was valued at USD 323.76 million in 2022 and expected to grow at a CAGR of 25.4% during the forecast period.
Types of Connectors:
Type 1 (SAE J1772): Primarily used in North America and Japan, Type 1 connectors have five or seven pins and are typically found on older electric vehicles or plug-in hybrids.
Type 2 (IEC 62196 or Mennekes): Commonly used in Europe, Type 2 connectors have seven pins and are used in both AC and DC charging scenarios. They are also becoming more prevalent in other regions.
CHAdeMO: CHAdeMO connectors are specifically used for DC fast charging and are common in Japanese and Korean electric vehicles.
Combined Charging System (CCS): CCS connectors are widely adopted in Europe and North America. They combine the Type 2 connector for AC charging with additional DC charging pins. CCS is capable of both AC and DC charging.
Cable Length:
EV charging cables come in various lengths, typically ranging from 5 meters (16 feet) to 10 meters (32 feet). Longer cables provide flexibility for parking and reaching charging stations in various locations.
Charging Speeds:
Charging cables support different charging speeds depending on the capabilities of the vehicle and the charging infrastructure.
AC Charging: AC charging cables usually support charging speeds from 3 kW to 22 kW, with 7 kW being the most common. However, higher-power charging stations can support up to 43 kW or more.
DC Fast Charging: DC charging cables, especially those compatible with CCS or CHAdeMO connectors, can support much higher charging speeds, ranging from 50 kW to over 350 kW in the latest charging stations.
Cable Construction:
EV charging cables are designed to be durable and able to withstand various weather conditions and frequent use.
They typically consist of an outer insulation layer made of thermoplastic or rubber material for protection.
Inside the cable, there are multiple conductors that carry the electric current and data signals required for communication between the vehicle and the charging station.
Safety Features:
EV charging cables incorporate safety features to ensure secure and reliable charging.
They have built-in mechanisms to prevent overcurrent, overheating, and overvoltage situations, protecting both the vehicle and the charging infrastructure.
Many cables also have additional features like locking mechanisms or tamper-proof designs to prevent unauthorized access or accidental disconnection during charging.
Report Attributes | Description |
Market Size in 2022 | USD 323.76 Million |
Market Forecast in 2031 | USD 732.67 Million |
CAGR % 2023-2031 | 25.4% |
Base Year | 2022 |
Historic Data | 2019-2021 |
Forecast Period | 2023-2031 |
Report USP | Production, Consumption, company share, company heatmap, company production capacity, growth factors and more |
Segments Covered | By Power Supply, By Length, By Charging Level, By Shape, By Application |
Regional Scope | North America, Europe, APAC, South America and Middle East and Africa |
Country Scope | U.S.; Canada; U.K.; Germany; France; Italy; Spain; Benelux; Nordic Countries; Russia; China; India; Japan; South Korea; Australia; Indonesia; Thailand; Mexico; Brazil; Argentina; Saudi Arabia; UAE; Egypt; South Africa; Nigeria |
Key Companies | Leoni AG Coroplast Chengdu Khons Technology Co., Ltd. Phoenix Contact Aptiv BESEN-Group General Cable Technologies Corporation Dyden Corporation TE Connectivity Others |
Covid-19 Impact:
The COVID-19 pandemic has had both positive and negative impacts on the electric vehicle (EV) charging cables market.
Temporary Slowdown: Like many industries, the EV market experienced a temporary slowdown during the initial phases of the pandemic. Production and distribution of EVs and related components, including charging cables, were disrupted due to factory closures, supply chain interruptions, and reduced consumer demand.
Recovery and Resilience: As economies began recovering and EV adoption continued to grow, the EV charging cables market showed resilience. Governments worldwide recognized the importance of clean transportation and implemented stimulus packages and incentives to promote EV adoption, which indirectly benefited the charging infrastructure, including charging cables.
Increased Emphasis on Clean Transportation: The pandemic has heightened global awareness of the need to reduce air pollution and mitigate climate change. As a result, there has been increased emphasis on transitioning to clean transportation, including EVs. This focus has positively influenced the EV charging cables market, as more charging stations and infrastructure are being deployed to support the growing EV fleet.
Rise in Home Charging: With lockdowns and restrictions in place, many people began working from home, resulting in a higher demand for home charging solutions. This trend led to an increased demand for residential charging cables, enabling EV owners to conveniently charge their vehicles at home.
Shift towards Contactless Charging: The pandemic accelerated the adoption of contactless and touchless technologies in various sectors. In the EV charging space, there has been a growing interest in wireless charging technologies, eliminating the need for physical charging cables. However, wireless charging is still in its early stages and has not significantly impacted the traditional charging cable market.
Supply Chain Challenges: The pandemic exposed vulnerabilities in global supply chains, impacting the availability of raw materials, components, and manufacturing capabilities. These challenges have affected the production and availability of EV charging cables, leading to potential delays or supply constraints.
EV Infrastructure Investments: Despite the pandemic, governments and private entities have continued to invest in EV infrastructure development, including charging stations. This investment has contributed to the demand for EV charging cables, as more charging points require adequate cable infrastructure to support EV charging.
Overall, while the COVID-19 pandemic initially impacted the EV charging cables market, the long-term outlook remains positive due to the increasing adoption of electric vehicles, government initiatives, and the ongoing focus on sustainable transportation.
Market Dynamics:
Drivers:
Increasing Electric Vehicle Adoption: The growing popularity and adoption of electric vehicles are major drivers for the EV charging cables market. As more consumers and businesses transition to electric vehicles, there is a higher demand for charging infrastructure, including charging cables, to support the charging needs of the expanding EV fleet.
Government Initiatives and Regulations: Governments around the world are implementing various initiatives and regulations to promote electric vehicle adoption and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. These measures include financial incentives, subsidies, tax benefits, and regulations mandating the installation of EV charging infrastructure in public spaces and commercial buildings. Such policies drive the demand for EV charging cables to support the expanding charging network.
Advancements in Charging Technology: Ongoing advancements in EV charging technology, particularly in fast-charging capabilities, are driving the demand for advanced charging cables. Higher-power charging stations, including those that support DC fast charging, require robust and capable charging cables to handle the increased electrical load and ensure safe and efficient charging.
Increasing Charging Infrastructure Investments: Investments in charging infrastructure are crucial for the widespread adoption of electric vehicles. Governments, utility companies, and private entities are investing in the deployment of charging stations in public spaces, residential areas, workplaces, and along highways. This infrastructure expansion creates a significant demand for charging cables to connect the charging stations with EVs.
Rising Demand for Home Charging: Many EV owners prefer the convenience and cost savings of charging their vehicles at home. The increasing popularity of home charging solutions drives the demand for residential charging cables. EV owners require reliable and efficient charging cables that enable them to conveniently charge their vehicles in their residential settings.
Technological Advancements in Charging Cables: The EV charging cables market is witnessing advancements in cable design, materials, and safety features. Manufacturers are developing cables that are more durable, flexible, and capable of handling higher charging speeds. Improved safety features, such as temperature monitoring and automatic shut-off mechanisms, ensure safe charging experiences.
Growing Environmental Concerns: Rising environmental concerns and the need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions are driving the transition to electric vehicles. Electric vehicles offer a more sustainable transportation solution compared to conventional internal combustion engine vehicles. The awareness of the environmental benefits of EVs fuels the demand for EV charging cables to support the charging infrastructure necessary for a cleaner transportation ecosystem.
Restraints:
Cost and Affordability: The cost of EV charging cables can be a restraining factor, particularly for consumers and businesses on a tight budget. High-quality charging cables with advanced features can be relatively expensive, which may discourage some potential buyers from investing in them. Price sensitivity can affect the adoption of EV charging cables, especially in regions where EV market penetration is still in its early stages.
Limited Charging Infrastructure: Despite the growing deployment of charging infrastructure, there are still regions and areas with limited charging stations. The lack of sufficient charging infrastructure can restrain the demand for EV charging cables, as consumers may be hesitant to invest in them if convenient charging options are not readily available.
Compatibility Issues: The EV market consists of various charging standards and connector types, which can lead to compatibility issues. Different vehicles may require specific charging cable connectors, such as Type 1, Type 2, CHAdeMO, or CCS. This fragmentation can create confusion for consumers, making it challenging to find the right charging cables for their specific vehicles and limiting the overall market size.
Range Anxiety and Charging Speed: Range anxiety, or the fear of running out of battery power without access to a charging station, is still a concern for some potential EV buyers. This anxiety is often related to the perceived limited range of electric vehicles and the time required for charging. The perception that charging is time-consuming compared to refueling at a gas station can be a restraining factor for the EV charging cables market.
Infrastructure Upgrades and Grid Constraints: As the adoption of electric vehicles increases, the demand on the electrical grid can rise significantly. In some cases, the existing electrical infrastructure may require upgrades to support the higher power demands of charging stations. Infrastructure upgrades can be costly and time-consuming, potentially delaying the deployment of charging stations and impacting the demand for charging cables.
Technological Limitations: While EV charging technology is advancing rapidly, there are still certain technological limitations that can impact the EV charging cables market. For example, wireless charging technology, while promising, is still in its early stages and not widely adopted. Technological challenges, such as charging efficiency, compatibility, and safety considerations, can impact the overall demand for charging cables.
Regulatory and Permitting Challenges: The installation of charging infrastructure, including charging stations, often requires compliance with various regulations and obtaining permits. Regulatory complexities and delays in permitting processes can hinder the expansion of charging infrastructure, indirectly impacting the demand for EV charging cables.
Lack of Standardization: While there are standard charging connectors like Type 1, Type 2, CHAdeMO, and CCS, there can still be variations in charging protocols, power levels, and communication standards among different charging stations and vehicles. This lack of standardization can create challenges in interoperability and compatibility, leading to confusion and uncertainty for consumers, impacting the demand for charging cables.
Regional Analysis:
North America: The United States and Canada have been witnessing significant growth in EV adoption, supported by government incentives and regulations promoting clean transportation.
There is a mix of charging standards, including Type 1 and Type 2 connectors, but the trend is shifting toward the adoption of Combined Charging System (CCS) connectors for both AC and DC charging.
Home charging solutions and workplace charging infrastructure are driving the demand for residential charging cables and commercial charging cables.
Europe: Europe is one of the leading regions in terms of EV adoption and charging infrastructure development.
The market for EV charging cables in Europe is driven by strong government support, regulations mandating the installation of charging infrastructure, and financial incentives.
Type 2 connectors are widely used in Europe for both AC and DC charging, and CCS connectors have gained significant traction due to their compatibility with a wide range of vehicles.
Countries like Norway, Germany, the Netherlands, and the United Kingdom are among the leaders in EV adoption and charging infrastructure deployment, contributing to the demand for charging cables.
Asia Pacific: Asia Pacific has seen rapid growth in the EV market, particularly in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea.
China is the largest EV market globally, driving the demand for EV charging cables. The market is supported by government initiatives and a growing charging infrastructure network.
CHAdeMO connectors are commonly used in Japanese and Korean EVs, while China primarily uses its own GB/T connector standard.
The region also experiences significant growth in home charging solutions, leading to the demand for residential charging cables.
Rest of the World: Other regions, such as Latin America, the Middle East, and Africa, are in the early stages of EV adoption but are gradually witnessing growth.
These regions are investing in charging infrastructure development and implementing policies to promote EV adoption, which will drive the demand for EV charging cables in the future.
The choice of charging connectors may vary across different countries within these regions, depending on regional standards and vehicle models available.
Competitive Landscape:
The global Electric Vehicle Charging Cables market is highly competitive and fragmented with the presence of several players. These companies are constantly focusing on new product development, partnerships, collaborations, and mergers and acquisitions to maintain their market position and expand their geographical presence.
Some of the key players operating in the market are:
• Leoni AG
• Coroplast
• Chengdu Khons Technology Co., Ltd.
• Phoenix Contact
• Aptiv
• BESEN-Group
• General Cable Technologies Corporation
• Dyden Corporation
• TE Connectivity
• Others
Segments
By Power Supply
• Alternate Charging (AC)
• Direct Charging (DC)
By Cable Length
• Below 5 meters
• 6 meters to 10 meters
• Above 10 meters
By Shape Outlook
• Straight Cable
• Coiled Cable
By Application
• Private Charging
• Public Charging
By Charging Level
• Level 1
• Level 2
• Level 3
By Geography
• North America
o U.S.
o Canada
o Mexico
• Europe
o U.K.
o Germany
o France
o Italy
o Spain
o Russia
• Asia-Pacific
o Japan
o China
o India
o Australia
o South Korea
o ASEAN
o Rest of APAC
• South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Rest of South America
• MEA
o South Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Egypt
o Rest of MEA
Quality Assurance Process
- We Market Research’s Quality Assurance program strives to deliver superior value to our clients.
We Market Research senior executive is assigned to each consulting engagement and works closely with the project team to deliver as per the clients expectations.
Market Research Process
We Market Research monitors 3 important attributes during the QA process- Cost, Schedule & Quality. We believe them as a critical benchmark in achieving a project’s success.
To mitigate risks that can impact project success, we deploy the follow project delivery best practices:
- Project kickoff meeting with client
- Conduct frequent client communications
- Form project steering committee
- Assign a senior SR executive as QA Executive
- Conduct internal editorial & quality reviews of project deliverables
- Certify project staff in SR methodologies & standards
- Monitor client satisfaction
- Monitor realized value post-project
Case Study- Automotive Sector
One of the key manufacturers of automotive had plans to invest in electric utility vehicles. The electric cars and associated markets being a of evolving nature, the automotive client approached We Market Research for a detailed insight on the market forecasts. The client specifically asked for competitive analysis, regulatory framework, regional prospects studied under the influence of drivers, challenges, opportunities, and pricing in terms of revenue and sales (million units).
Solution
The overall study was executed in three stages, intending to help the client meet its objective of precisely understanding the entire market before deciding on an investment. At first, secondary research was conducted considering political, economic, social, and technological parameters to get a gist of the various aspects of the market. This stage of the study concluded with the derivation of drivers, opportunities, and challenges. It also laid substantial emphasis on understanding and collecting data not only on a global scale but also on the regional and country levels. Data Extraction through Primary Research
The second stage involved primary research in which several market players and automotive parts suppliers were contacted to study their viewpoint concerning the development of their market and production capacity, clientele, and product line. This stage concluded in a brief understanding of the competitive ecosystem and also glanced through the strategies and pricing of the companies profiled.
Market Estimates and Forecast
In the final stage of the study, market forecasts for the electric utility were derived using multiple market engineering approaches. This data helped the client to get an overview of the market and accelerate the process of investment.
Case Study- ICT Sector
Business process outsourcing, being one of the lucrative markets from both supply- and demand- side, has appealed to various companies. One of the prominent corporations based out of Japan approached us with their requirements regarding the scope of the procurement outsourcing market for around 50 countries. Additionally, the client also sought key players operating in the market and their revenue breakdown in terms of region and application.
Business Solution
An exhaustive market study was conducted based on primary and secondary research that involved factors such as labor costs in various countries, skilled and technical labors, manufacturing scenario, and their respective contributions in the global GDP. A comparative study of the market was conducted from both supply- and demand side, with the supply-side comprising of notable companies, such as GEP, Accenture, and others, that provide these services. On the other hand, large manufacturing companies from them demand-side were considered that opt for these services.
Conclusion
The report aided the client in understanding the market trends, including country-level business scenarios, consumer behavior, and trends in 50 countries. The report also provided financial insights of crucial players and detailed market estimations and forecasts till 2033.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the market size and growth projections?
The global Electric Vehicle Charging Cables market was valued at USD 323.76 million in 2022 and expected to grow at a CAGR of 25.4% during the forecast period.
What are the drivers shaping various markets?
The growing popularity and adoption of electric vehicles are major drivers for the EV charging cables market.
Who are the key competitors of market Players?
Some of the major players operating within the market are Leoni AG,Coroplast,Chengdu Khons Technology Co., Ltd.,Phoenix Contact,Aptiv,BESEN-Group,General Cable Technologies Corporation,Dyden Corporation,TE Connectivity,Others
What are the top performing segments, and countries / regions of each of the markets?
The United States and Canada have been witnessing significant growth in EV adoption, supported by government incentives and regulations promoting clean transportation.
}})
Select a license type that suits your business needs
US $3499
Only Three Thousand Four Hundred Ninety Nine US dollar
- 1 User access
- 15% Additional Free Customization
- Free Unlimited post-sale support
- 100% Service Guarantee until achievement of ROI
US $4499
Only Four Thousand Four Hundred Ninety Nine US dollar
- 5 Users access
- 25% Additional Free Customization
- Access Report summaries for Free
- Guaranteed service
- Dedicated Account Manager
- Discount of 20% on next purchase
- Get personalized market brief from Lead Author
- Printing of Report permitted
- Discount of 20% on next purchase
- 100% Service Guarantee until achievement of ROI
US $5499
Only Five Thousand Four Hundred Ninety Nine US dollar
- Unlimited User Access
- 30% Additional Free Customization
- Exclusive Previews to latest or upcoming reports
- Discount of 30% on next purchase
- 100% Service Guarantee until achievement of ROI