
3D Barcode Reader Market Analysis By Component (Hardware, Software, Services), By Technology (Laser Scanners, Imaging Scanners, Others), By End-user (Retail and E-commerce, Manufacturing, Healthcare, BFSI, IT & Telecommunication, Transportation and Logistics, Others) & Forecast By 2031
- PUBLISHED ON
- 2024-06-06
- NO OF PAGES
- 283
- CATEGORY
- Electronics & Communication
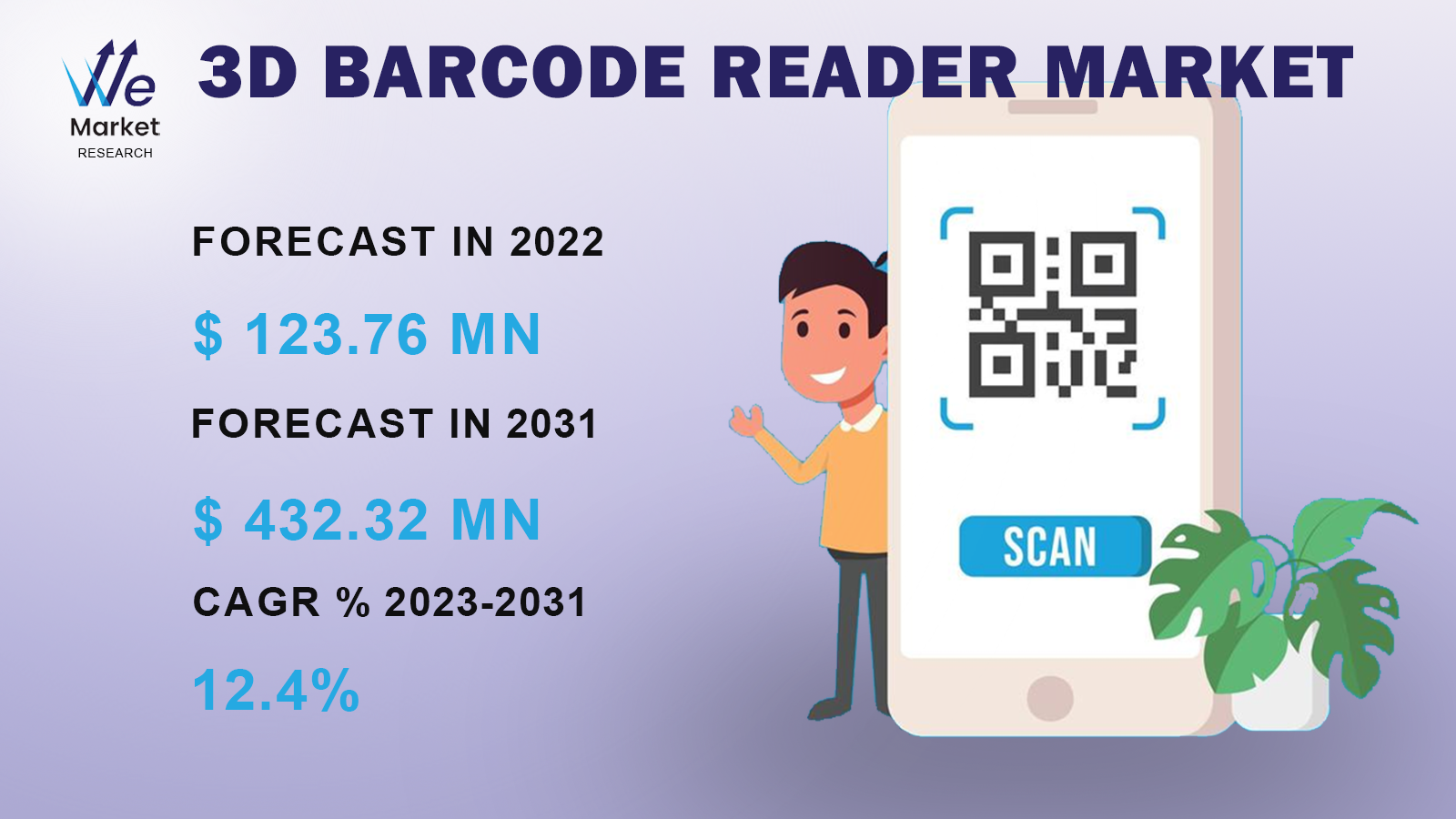
The global 3D Barcode Reader market was valued at USD 123.76 million in 2022 and expected to grow at a CAGR of 12.4% during the forecast period. A 3D barcode reader, also known as a 3D imaging barcode scanner, is a device used to capture and decode barcodes in three dimensions. Unlike traditional 1D or 2D barcode scanners, which read barcodes in a flat plane, 3D barcode readers can read barcodes regardless of their orientation, angle, or position.
Imaging Technology: 3D barcode readers utilize advanced imaging technology, such as laser or camera-based systems, to capture three-dimensional images of barcodes. These devices can capture barcode data from various angles and orientations, making them highly versatile for scanning barcodes on objects of different shapes, sizes, and surfaces.
Flexibility and Versatility: 3D barcode readers are designed to read barcodes in challenging environments and on objects with complex surfaces. They can read barcodes on curved surfaces, irregularly shaped objects, or items with reflective or uneven surfaces. This makes them suitable for industries like manufacturing, logistics, retail, and healthcare, where barcodes may be located in difficult-to-reach or non-standard positions.
High-Speed Scanning: 3D barcode readers are equipped with fast image capture and processing capabilities, allowing for rapid scanning and decoding of barcodes. This speed is crucial in industries that require quick and efficient barcode scanning, such as high-volume manufacturing or warehouse operations.
Decoding Capabilities: 3D barcode readers can decode various types of barcodes, including traditional 1D barcodes (such as UPC or EAN codes) and 2D barcodes (such as QR codes or DataMatrix codes). They can also read barcodes with damaged, faded, or partially obscured elements, ensuring accurate data capture even in challenging conditions.
Connectivity and Integration: Many 3D barcode readers offer connectivity options such as USB, Bluetooth, or wireless connections, enabling seamless integration with other devices and systems. This allows for real-time data transfer, compatibility with existing software applications, and integration with inventory management or point-of-sale systems.
Application-Specific Features: Depending on the industry and use case, 3D barcode readers may have additional features tailored to specific requirements. For example, some devices may have ruggedized designs to withstand harsh environments, built-in illumination for low-light scanning, or the ability to read barcodes from long distances.
Improved Efficiency and Accuracy: By offering increased flexibility and versatility in barcode scanning, 3D barcode readers can improve efficiency and accuracy in various operations. They reduce the need for manual adjustment or alignment of objects for scanning, minimize errors due to barcode misreads, and enhance productivity in industries that heavily rely on barcode scanning for inventory management, traceability, and quality control.
Report Attributes | Description |
Market Size in 2022 | USD 123.76 Million |
Market Forecast in 2031 | USD 432.32 Million |
CAGR % 2023-2031 | 12.4% |
Base Year | 2022 |
Historic Data | 2019-2021 |
Forecast Period | 2023-2031 |
Report USP | Production, Consumption, company share, company heatmap, company production capacity, growth factors and more |
Segments Covered | By Component, By Technology, By End-user |
Regional Scope | North America, Europe, APAC, South America and Middle East and Africa |
Country Scope | U.S.; Canada; U.K.; Germany; France; Italy; Spain; Benelux; Nordic Countries; Russia; China; India; Japan; South Korea; Australia; Indonesia; Thailand; Mexico; Brazil; Argentina; Saudi Arabia; UAE; Egypt; South Africa; Nigeria |
Key Companies | Cognex Corporation Zebra Technologies Corporation Datalogic S.p.A. Honeywell International Inc. Keyence Corporation Sick AG Opticon Sensors Europe B.V. Newland EMEA Zebex Industries Inc. Code Corporation Others |
Covid-19 Impact:
Increased Focus on Hygiene and Contactless Operations: In response to the pandemic, there has been a heightened emphasis on hygiene and minimizing physical contact. This has led to a greater demand for contactless technologies, including barcode scanning solutions. 3D barcode readers can be used in a contactless manner, allowing users to scan barcodes without physically touching them. This feature aligns with the need for enhanced safety measures during the pandemic.
Shift in Industries and Applications: The pandemic has caused significant disruptions in various industries, resulting in shifts in priorities and applications for barcode scanning technologies. For example, industries such as healthcare and e-commerce experienced a surge in demand, leading to an increased need for advanced barcode scanning solutions, including 3D barcode readers. These readers can be utilized for tasks such as tracking medical supplies or handling high-volume e-commerce orders.
Supply Chain Challenges: The pandemic has disrupted global supply chains, impacting the availability and delivery of various products, including 3D barcode readers. Manufacturing and distribution delays, logistical challenges, and increased demand for certain technologies have affected the supply chain of barcode scanning devices. This may have led to delays in product availability or increased prices.
Shift to Remote Work and Automation: With the rise of remote work and social distancing measures, there has been a greater focus on automation and digital solutions. Barcode scanning technologies, including 3D barcode readers, have become even more relevant in enabling remote operations, inventory management, and supply chain tracking. Businesses have been adopting automated systems to reduce physical contact and enhance efficiency in barcode scanning processes.
Adoption Challenges and Budget Constraints: The economic impact of the pandemic has caused budget constraints for many businesses. The implementation of new technologies, including 3D barcode readers, may have been delayed or put on hold due to financial challenges. The uncertainty and disruptions caused by the pandemic may have resulted in businesses prioritizing essential operations over technology upgrades.
Innovation and Advancements: Despite the challenges posed by the pandemic, there have been ongoing innovations and advancements in barcode scanning technologies, including 3D barcode readers. Manufacturers have been focusing on developing more advanced features, improved scanning speed, and enhanced integration capabilities to meet evolving customer needs in a post-pandemic world.
Market Dynamics:
Drivers:
Increasing Need for Efficiency and Accuracy: 3D barcode readers offer enhanced efficiency and accuracy in barcode scanning compared to traditional 1D or 2D scanners. Their ability to read barcodes from multiple angles and orientations, regardless of the object's position or surface, reduces the need for manual adjustment and alignment. This improves operational efficiency and reduces errors in data capture, making 3D barcode readers attractive to industries that rely on accurate and efficient barcode scanning.
Expansion of E-commerce and Retail Industry: The growth of e-commerce and online retail has increased the demand for advanced barcode scanning solutions. 3D barcode readers enable quick and accurate scanning of barcodes on various package sizes, shapes, and surfaces, facilitating efficient inventory management, order processing, and shipment tracking in the e-commerce and retail sectors.
Industry-Specific Applications: Different industries have unique barcode scanning requirements, and 3D barcode readers offer solutions for specific applications. For example, in the healthcare industry, 3D barcode readers can be used to scan barcodes on irregularly shaped medical devices, pharmaceutical products, or patient wristbands. In manufacturing and logistics, these scanners enable efficient tracking and traceability of items with complex surfaces or unconventional barcode placements.
Advancements in Imaging Technology: Technological advancements in imaging technology, such as high-resolution cameras and sophisticated algorithms, have improved the capabilities of 3D barcode readers. These advancements have resulted in faster scanning speeds, higher accuracy rates, and improved decoding capabilities, making 3D barcode readers more attractive to businesses looking to enhance their scanning processes.
Safety and Hygiene Considerations: The COVID-19 pandemic has increased the focus on safety and hygiene in various industries. 3D barcode readers offer a contactless scanning option, minimizing physical contact and reducing the risk of cross-contamination. This feature aligns with the heightened awareness of health and safety measures and the need for touch-free solutions in industries like healthcare, hospitality, and retail.
Integration with Other Systems: 3D barcode readers are often designed to integrate with other systems, such as inventory management software, point-of-sale systems, or enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems. Seamless integration allows for real-time data transfer, improved workflow efficiency, and enhanced decision-making capabilities, driving the adoption of 3D barcode readers in businesses looking for a holistic solution to manage their operations.
Cost Reduction and Return on Investment: As technology advances and becomes more accessible, the cost of 3D barcode readers has decreased over time. The potential cost savings and return on investment resulting from improved efficiency, reduced errors, and streamlined operations make 3D barcode readers an attractive option for businesses seeking to optimize their barcode scanning processes.
Restraints:
Cost: 3D barcode readers can be more expensive compared to traditional 1D or 2D barcode scanners. The advanced imaging technology, hardware components, and additional features of 3D barcode readers contribute to their higher price point. This cost factor can be a deterrent for businesses, particularly smaller or budget-constrained organizations, limiting their adoption of 3D barcode readers.
Implementation Challenges: Implementing 3D barcode readers can come with certain challenges. Integration with existing systems, such as inventory management or point-of-sale systems, may require additional effort and resources. Some businesses may face compatibility issues with their current infrastructure, leading to delays or complications in the implementation process.
Training and Familiarity: Adopting new technology, including 3D barcode readers, requires training and familiarization for the staff. Employees need to learn how to use the devices, understand the scanning capabilities, and interpret the data captured by the readers. Training programs and resources need to be allocated, and time needs to be invested to ensure a smooth transition. Resistance or difficulty in training staff can impede the adoption of 3D barcode readers.
Limited Industry Awareness: While 3D barcode readers offer advanced scanning capabilities, their awareness and understanding may be limited in some industries. Businesses may not be aware of the benefits and use cases of 3D barcode readers or may not fully comprehend their potential impact on operational efficiency and accuracy. This lack of awareness can slow down the adoption of 3D barcode readers as businesses stick with traditional scanning methods.
Market Fragmentation: The market for 3D barcode readers is relatively fragmented, with various manufacturers offering different models and technologies. This can make it challenging for businesses to choose the right solution that meets their specific requirements. The availability of multiple options and the lack of standardized features can create confusion and indecision, delaying the adoption of 3D barcode readers.
Resistance to Change: Some businesses may have established workflows and processes that rely on traditional barcode scanning methods. The resistance to change or a preference for familiar systems can hinder the adoption of 3D barcode readers. The perceived risks or disruptions associated with implementing new technology can discourage businesses from exploring or investing in 3D barcode readers.
Regional Analysis:
North America: North America has been one of the leading regions in terms of the adoption and growth of 3D barcode readers. The region is characterized by a strong presence of industries such as manufacturing, logistics, retail, and healthcare, which are key users of barcode scanning technologies. The demand for 3D barcode readers in North America is driven by the need for efficient inventory management, supply chain tracking, and increased automation in various industries.
Europe: Europe is another significant market for 3D barcode readers. The region has a well-established retail sector, where barcode scanning plays a crucial role in inventory management and customer service. Additionally, industries such as automotive, pharmaceuticals, and logistics contribute to the demand for 3D barcode readers in Europe. The emphasis on efficiency, accuracy, and traceability further drives the adoption of advanced barcode scanning solutions in the region.
Asia Pacific: The Asia Pacific region is experiencing rapid growth in the adoption of 3D barcode readers. The region is home to major manufacturing hubs, e-commerce giants, and logistics companies. The increasing demand for efficient supply chain management, inventory tracking, and automation is fueling the adoption of 3D barcode readers in countries like China, Japan, South Korea, and India. The region also presents significant growth opportunities due to the increasing penetration of e-commerce and the rising need for traceability in the food and healthcare sectors.
Latin America: Latin America is an emerging market for 3D barcode readers. The region's retail sector, manufacturing industry, and logistics operations are driving the demand for efficient barcode scanning solutions. With the increasing focus on inventory optimization, improved customer service, and compliance with regulations, businesses in Latin America are adopting 3D barcode readers to enhance their operational efficiency and accuracy.
Middle East and Africa: The Middle East and Africa region also present opportunities for the growth of the 3D barcode reader market. Industries such as retail, healthcare, and logistics in this region are recognizing the benefits of advanced barcode scanning solutions in improving operational efficiency and inventory management. As businesses in the region strive for automation and digitalization, the adoption of 3D barcode readers is expected to increase.
Competitive Landscape:
The global 3D Barcode Reader market is highly competitive and fragmented with the presence of several players. These companies are constantly focusing on new product development, partnerships, collaborations, and mergers and acquisitions to maintain their market position and expand their geographical presence.
Some of the key players operating in the market are:
• Cognex Corporation
• Zebra Technologies Corporation
• Datalogic S.p.A.
• Honeywell International Inc.
• Keyence Corporation
• Sick AG
• Opticon Sensors Europe B.V.
• Newland EMEA
• Zebex Industries Inc.
• Code Corporation
• Others
Segments
By Component
• Hardware
• Software
• Services
By Technology
• Laser Scanners
• Imaging Scanners
• Others
By End-user
• Retail and E-commerce
• Manufacturing
• Healthcare
• BFSI
• IT & Telecommunication
• Transportation and Logistics
• Others
By Geography
• North America
o U.S.
o Canada
o Mexico
• Europe
o U.K.
o Germany
o France
o Italy
o Spain
o Russia
• Asia-Pacific
o Japan
o China
o India
o Australia
o South Korea
o ASEAN
o Rest of APAC
• South America
o Brazil
o Argentina
o Colombia
o Rest of South America
• MEA
o South Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Egypt
o Rest of MEA
Quality Assurance Process
- We Market Research’s Quality Assurance program strives to deliver superior value to our clients.
We Market Research senior executive is assigned to each consulting engagement and works closely with the project team to deliver as per the clients expectations.
Market Research Process
We Market Research monitors 3 important attributes during the QA process- Cost, Schedule & Quality. We believe them as a critical benchmark in achieving a project’s success.
To mitigate risks that can impact project success, we deploy the follow project delivery best practices:
- Project kickoff meeting with client
- Conduct frequent client communications
- Form project steering committee
- Assign a senior SR executive as QA Executive
- Conduct internal editorial & quality reviews of project deliverables
- Certify project staff in SR methodologies & standards
- Monitor client satisfaction
- Monitor realized value post-project
Case Study- Automotive Sector
One of the key manufacturers of automotive had plans to invest in electric utility vehicles. The electric cars and associated markets being a of evolving nature, the automotive client approached We Market Research for a detailed insight on the market forecasts. The client specifically asked for competitive analysis, regulatory framework, regional prospects studied under the influence of drivers, challenges, opportunities, and pricing in terms of revenue and sales (million units).
Solution
The overall study was executed in three stages, intending to help the client meet its objective of precisely understanding the entire market before deciding on an investment. At first, secondary research was conducted considering political, economic, social, and technological parameters to get a gist of the various aspects of the market. This stage of the study concluded with the derivation of drivers, opportunities, and challenges. It also laid substantial emphasis on understanding and collecting data not only on a global scale but also on the regional and country levels. Data Extraction through Primary Research
The second stage involved primary research in which several market players and automotive parts suppliers were contacted to study their viewpoint concerning the development of their market and production capacity, clientele, and product line. This stage concluded in a brief understanding of the competitive ecosystem and also glanced through the strategies and pricing of the companies profiled.
Market Estimates and Forecast
In the final stage of the study, market forecasts for the electric utility were derived using multiple market engineering approaches. This data helped the client to get an overview of the market and accelerate the process of investment.
Case Study- ICT Sector
Business process outsourcing, being one of the lucrative markets from both supply- and demand- side, has appealed to various companies. One of the prominent corporations based out of Japan approached us with their requirements regarding the scope of the procurement outsourcing market for around 50 countries. Additionally, the client also sought key players operating in the market and their revenue breakdown in terms of region and application.
Business Solution
An exhaustive market study was conducted based on primary and secondary research that involved factors such as labor costs in various countries, skilled and technical labors, manufacturing scenario, and their respective contributions in the global GDP. A comparative study of the market was conducted from both supply- and demand side, with the supply-side comprising of notable companies, such as GEP, Accenture, and others, that provide these services. On the other hand, large manufacturing companies from them demand-side were considered that opt for these services.
Conclusion
The report aided the client in understanding the market trends, including country-level business scenarios, consumer behavior, and trends in 50 countries. The report also provided financial insights of crucial players and detailed market estimations and forecasts till 2033.
}})
Select a license type that suits your business needs
US $3499
Only Three Thousand Four Hundred Ninety Nine US dollar
- 1 User access
- 15% Additional Free Customization
- Free Unlimited post-sale support
- 100% Service Guarantee until achievement of ROI
US $4499
Only Four Thousand Four Hundred Ninety Nine US dollar
- 5 Users access
- 25% Additional Free Customization
- Access Report summaries for Free
- Guaranteed service
- Dedicated Account Manager
- Discount of 20% on next purchase
- Get personalized market brief from Lead Author
- Printing of Report permitted
- Discount of 20% on next purchase
- 100% Service Guarantee until achievement of ROI
US $5499
Only Five Thousand Four Hundred Ninety Nine US dollar
- Unlimited User Access
- 30% Additional Free Customization
- Exclusive Previews to latest or upcoming reports
- Discount of 30% on next purchase
- 100% Service Guarantee until achievement of ROI