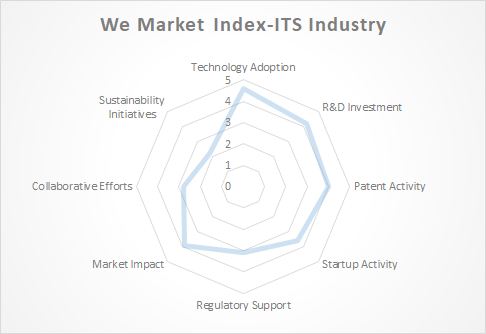
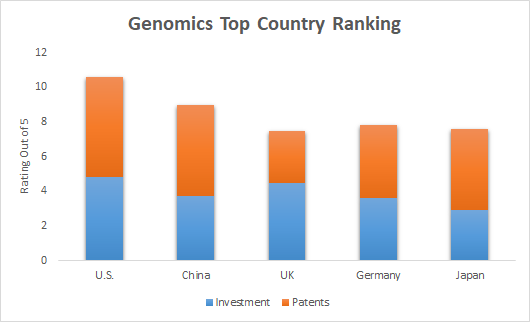
The Rise of Biosimilars: A Transformative Force in Healthcare
In
recent years, the biosimilars market has emerged as a significant player in the
pharmaceutical industry, promising both economic benefits and enhanced patient
access to crucial therapies. This blog explores the key aspects driving the
growth of biosimilars, their impact on healthcare systems, and future
prospects.
Understanding Biosimilars:
Biosimilars
are biological medicines that are highly similar to already approved biological
medicines, which are often referred to as reference or originator products.
Unlike generic drugs, which are exact copies of their chemical counterparts
(small molecule drugs), biosimilars are similar but not identical to their
reference products due to the complexity of biological molecules.
Biosimilars
are biological products that are highly similar to, and have no clinically
meaningful differences from, existing FDA-approved reference products. They are
designed to be analogous to generic versions of small molecule drugs but are
more complex due to their biological nature.
Impact on Healthcare Systems
The
adoption of biosimilars has profound implications for healthcare systems
globally:
Ø Improved Access: Biosimilars expand access to
essential therapies, particularly in areas where the cost of biologics may be
prohibitive.
Ø Market Competition: Increased competition
promotes price reductions for both biosimilars and originator biologics,
encouraging cost savings across healthcare budgets.
Ø Innovation and R&D: The revenue generated
from biosimilar sales can be reinvested in research and development (R&D)
for new therapies, fostering innovation in biotechnology.
Biosimilars Market Trends and Projections
The
Biosimilars market is predicted to develop at a compound annual growth rate
(CAGR) of 17.5% from 2024 to 2034, when it is projected to reach USD 1,247.94
Billion by 2034, based on an average growth pattern. The market is estimated to
reach a value of USD 32.78 Billion in 2024.
One
of the primary drivers behind the rise of biosimilars is their potential to
lower treatment costs significantly. By introducing competition to the market,
biosimilars offer cost-effective alternatives to expensive biologics, making
essential treatments more accessible to patients and healthcare systems
worldwide.
The
expiration of patents for blockbuster biologics has paved the way for
biosimilar developers to enter the market. This has led to a competitive
landscape where manufacturers can capitalize on their expertise in
biotechnology and regulatory compliance to bring affordable alternatives to
market faster.
Biosimilars for Cancer Treatment:
Biosimilars in cancer treatment
represent a significant advancement in oncology, offering comparable efficacy
and safety to expensive biologic drugs known as reference products. This
overview explores the role of biosimilars in cancer therapy, including their
development, regulatory considerations, market impact, and future prospects.
Biosimilars for cancer treatment
are biologic drugs that are highly similar to approved reference biologics used
in oncology, such as monoclonal antibodies and growth factors. They are
developed to provide cost-effective alternatives while maintaining equivalent
clinical outcomes in terms of efficacy and safety.
Several biosimilars
for cancer therapies:
- Trastuzumab Biosimilars: Used in the treatment of HER2-positive breast cancer, biosimilars
such as Ogivri (Mylan/Biocon) and Herzuma (Celltrion) have been approved
in various regions.
- Rituximab Biosimilars: Used in non-Hodgkin lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia,
biosimilars like Ruxience (Pfizer) and Truxima (Celltrion) provide
alternatives to Rituxan.
- Bevacizumab Biosimilars: Used in colorectal, lung, and renal cancers, biosimilars such as
Mvasi (Amgen/Allergan) and Zirabev (Pfizer) have been approved.
Case Study: Biosimilars Market - The Journey of Adalimumab Biosimilars
Adalimumab, marketed under the
brand name Humira by AbbVie, is a widely used biologic drug approved for
treating autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, and Crohn's
disease. With its patent expiration in various regions, the market for
adalimumab biosimilars has become a focal point due to its substantial global
sales and patient demand.
Humira was one of the top-selling
drugs globally, generating billions in revenue annually for AbbVie. As patents
began to expire starting in 2016 (in Europe), biosimilar developers saw an
opportunity to enter the market with more affordable alternatives.
Developing adalimumab biosimilars
involved rigorous comparative analytical studies, preclinical trials, and
clinical trials to demonstrate similarity to Humira in terms of safety,
efficacy, and immunogenicity. Regulatory authorities such as the FDA (in the
US) and the EMA (in Europe) set stringent guidelines for biosimilar approval,
requiring extensive data to ensure interchangeability and patient safety.
Conclusion
Biosimilars represent a promising
avenue in cancer treatment, offering cost-effective alternatives to expensive
biologic drugs while maintaining comparable clinical efficacy and safety
profiles. As the field advances, continued research, regulatory alignment, and
stakeholder education will be critical in maximizing the potential of
biosimilars to benefit cancer patients and healthcare systems worldwide.
While navigating regulatory
complexities and market access challenges, the biosimilars market presents
significant growth opportunities for pharmaceutical companies and healthcare
systems alike. As innovation and competition intensify, biosimilars continue to
reshape the landscape of biologic drug therapy, aiming to enhance affordability
and patient access worldwide.
The biosimilars market represents a
paradigm shift in healthcare, offering a balance between affordability and
innovation. As more biosimilars enter the market and gain acceptance, they have
the potential to redefine treatment standards and improve patient outcomes
globally. With ongoing advancements in biotechnology and regulatory frameworks,
the future of biosimilars holds promise for a more accessible and sustainable
healthcare landscape.
In summary, while challenges remain, the biosimilars market is poised for continued growth, offering a compelling alternative in the quest for accessible, high-quality healthcare solutions.